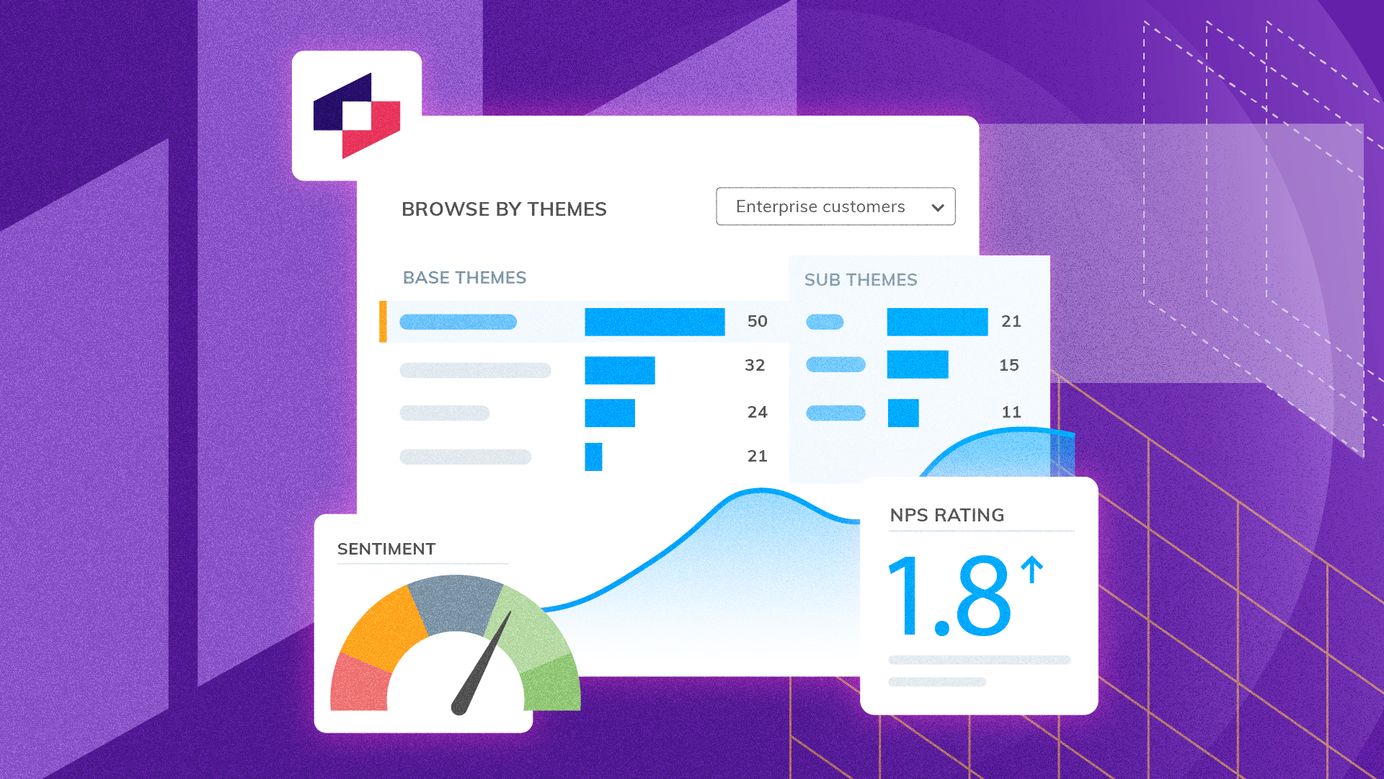
Understanding Qualitative vs Quantitative Data
Understanding how to use both qualitative and quantitative data can help you make better decisions and gain deeper insights. Here's what you need to know.
Keen to understand the difference between qualitative vs quantitative data?
There are many types of data out there! Understanding the best ways to use both qualitative and quantitative data can help you make better decisions and gain deeper insights.
In this post, I’ll take a closer look at these two types of data, exploring their differences, strengths, and how they can work together to provide a comprehensive understanding of complex issues.
TL;DR
- Qualitative data helps you understand people’s behaviors, emotions and experiences while quantitative data provides measurable insights.
- Qualitative research methods include interviews, focus groups, and surveys with open-ended questions, while quantitative research uses surveys with closed-ended questions.
- In simple terms, quantitative data answers the “what” or “how many” of a research question, and qualitative data answers the "why".
- Combining qualitative and quantitative data helps researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of any given subject.
Understanding Qualitative Data
Diving into qualitative data means exploring the rich, descriptive information that helps us understand human behavior, emotions, and experiences.
Unlike quantitative data, which focuses on numbers and measurements, qualitative data is all about the subjective. It captures people’s thoughts, feelings, and interactions with their environment.
Qualitative data can be collected through interviews, focus groups, surveys, and observations. It can provide insights into why people do what they do, how they feel about certain topics, and how they interact with their environment.
This type of data is important no matter the industry - from product managers looking to improve an app, to healthcare professionals wanting to transform the in-patient experience.
Defining Qualitative Data
So what exactly is qualitative data? At its core, qualitative data is descriptive, non-numerical information that helps us understand complex social phenomena. It refers to the words, phrases, or labels used to describe certain characteristics or traits, such as people’s opinions, motivations, and emotions.
Qualitative research is subjective, less rigid, and approaches the research topic from the perspective of those living it. While quantitative data focuses on numbers and measuring variables, qualitative data allows you to gain a deeper understanding of the topic at hand and grasp the context in which it exists.
Common Qualitative Research Methods
There are several types of qualitative feedback that can help you uncover deep insights into human experiences. These qualitative feedback types include in-depth interviews, focus groups, surveys, observations, and case studies:
- Interviews in qualitative research dive into people’s attitudes and opinions on specific topics, allowing the researcher to explore their unique perspectives.
- Focus groups gather information through group discussions where participants share their thoughts and ideas.
- Qualitative surveys are surveys with open-ended questions, or 'open-enders'. This means a question like 'What impressed you?' where the respondent can provide their own verbatim answer.
- Observations involve watching people in their natural settings to collect data.
- Case studies analyze a single person or group in detail.
These types of qualitative feedback offer rich, in-depth insights that help researchers gain a better understanding of complex social phenomena and interactions with products or services.
There are also a few different methods & approaches of qualitative data analysis.
Analyzing Qualitative Data
When it comes to analyzing qualitative data, the process involves interpreting unstructured data, such as large chunks of text. This requires a different approach than that used for quantitative data.
Popular techniques for qualitative data analysis include content analysis, grounded theory, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis.
Thematic analysis, for example, is a widely used method that involves coding the data to identify common keywords or topics and then grouping them into meaningful themes.
While traditionally known for being time-consuming, qualitative data analysis plays a crucial role in uncovering the hidden gems of information that can lead to valuable insights and understanding.
And with advances in technology, it's now possible to analyze qualitative data at scale, faster than ever before. For example, here at Thematic we take millions of customer comments - large volumes of hard to analyze, unstructured text data - and use AI to turn them into quantifiable insights for product companies to act on.
Grasping Quantitative Data

Okay, now for quantitative data. The focus here is on numerical information that allows you to measure variables, test hypotheses, and establish general patterns across populations.
Quantitative data offers an objective and reliable approach to research, providing measurable and statistically significant insights that can help drive informed decision-making.
Defining Quantitative Data
Quantitative data is numerical and measurable information that can be used to identify trends, relationships, and make predictions. This type of data is the cornerstone of quantitative research, which relies on gathering numerical data and using statistical methods to analyze it.
Some examples of quantitative data include age, height, weight, income, and test scores. This data is often used to analyze relationships, confirm or test theories or hypotheses, assess problems, or answer the “what” or “how many” of a research question.
Quantitative data allows for quantifying behaviors, opinions, attitudes, and other variables, making it an essential tool in many research and business contexts.
Common Quantitative Research Methods
There are several quantitative research methods you can employ to gather numerical data. Experiments, numerical observations and surveys comprising closed-ended questions are some common methods. They can be beneficial in providing accurate empirical data.
Surveys, in particular, are a popular research method involving the use of structured questions to collect information from a large number of participants.
Closed-ended questions are those where the respondent has to choose from a set of pre-defined answers. Think multi-choice options, yes/no, true/false, or a scale, like 'how likely are you to recommend us to family or friends', where 1 is least likely, and 10 is most likely. Closed-ended questions provide respondents with a clear direction and help ensure consistency in the data collected, making it easier to analyze.
Other examples of quantitative research methods include controlled observations and questionnaires, which can help measure variables, test hypotheses, and establish general patterns across populations.
Analyzing Quantitative Data
When it comes to analyzing quantitative data, researchers typically rely on descriptive and evidence-based statistics to summarize data patterns and identify significant differences between groups. Through statistical analysis, researchers can draw conclusions from the numerical data, spot trends, see relationships, and make predictions.
Statistical analysis techniques help quantitative researchers make informed decisions based on measurable and objective data.
Comparing and Contrasting Qualitative and Quantitative Data

Now that we have a good understanding of both qualitative and quantitative data, let’s dive deeper into their differences, as well as how they can complement each other.
Recognizing the key distinctions between these two types of data is essential for choosing the right research methods and analysis techniques for a specific research question or project.
Differences in Data Collection
One of the main differences between qualitative and quantitative data collection lies in the methods used.
Qualitative data collection methods involve:
- Surveys with open-ended questions
- Observations
- Interviews
All of which allow for more flexibility and adaptability in the research process. These approaches capture people’s thoughts, feelings, and experiences, providing a rich and in-depth understanding.
Quantitative data collection methods involve:
- Structured surveys
- Experiments with numerical data
- Statistical analysis.
These approaches focus on measuring variables and testing hypotheses, providing an objective and reliable set of data that can be easily compared and analyzed.
The choice between qualitative and quantitative data collection methods largely depends on the research question and the type of insights the researcher aims to gain.
Differences in Data Analysis
In terms of data analysis, qualitative and quantitative data require different approaches and techniques.
Qualitative data analysis involves interpreting non-numerical data, often through the use of interpretive techniques such as:
- Content analysis
- Grounded theory
- Thematic analysis
- Discourse analysis.
This type of analysis aims to uncover deeper insights and understanding by exploring the nuances and complexities of the data.
Qualitative data is the best choice when you're looking to understand complex social phenomena, explore new ideas, or gain insights into human experiences and emotions. This type of data allows you to dive into the subjective nature of experiences and capture the essence of people’s thoughts, feelings, and interactions with their environment.
By using qualitative data, you get a deeper understanding of the context surrounding an issue. You can uncover hidden patterns and relationships that may not be immediately apparent through quantitative data alone. This depth of understanding can prove invaluable in informing decision-making and guiding future research efforts.
In contrast, quantitative data analysis relies on statistical methods to analyze numerical data. This objective approach allows researchers to identify patterns, connections, and predict outcomes based on the data.
Quantitative data is the best choice when the goal is to measure variables, test hypotheses, and establish general patterns across populations. This type of data allows for the collection of objective, measurable information that can be easily compared and analyzed, providing insights into trends, relationships, and predictive outcomes.
Quantitative data is particularly useful for confirming or testing theories or hypotheses, assessing problems, and answering the “what” or “how many” of a research question. By using quantitative data, researchers can quantify behaviors, opinions, attitudes, and other variables, allowing them to make informed decisions based on measurable and reliable data.
While both types of data analysis have their merits, it’s important to recognize the unique strengths and limitations of each approach to ensure the most effective and accurate analysis of your data.
Complementing Each Other: Implementing Mixed Methods Research
It doesn't always have to be qualitative vs quantitative. There are clear differences in their collection and analysis methods, but both types of data can work together to provide a more comprehensive understanding of research questions.
By employing qualitative and quantitative research, qualitative data offers depth and context, allowing researchers to explore the reasons behind trends, behaviors, and opinions, while quantitative data provides measurable trends and patterns that can be used to make predictions and draw conclusions.
In customer feedback analysis, combining qualitative and quantitative data is the best way to get a 360 view of your users. Feedback analysis software makes it easy to combine your qualitative data with quantitative data for deeper insights.
Metrics go up, and metrics go down - this is your quantitative data. Numbers on a dashboard provide a good indicator of various things going wrong - and going right - but you need to know why they’re shifting.
You can draw some conclusions from your quantitative data, such as comparing customer segments to work out common patterns, but what you need to know is how to shift your numbers in a positive direction.
Your much harder to analyze qualitative data is where the answers lie. Qualitative data provides valuable context, so that you get the insight you need into the customer experience and understand the "why" behind what's happening with your metrics.
Real-World Examples of Qualitative and Quantitative Data
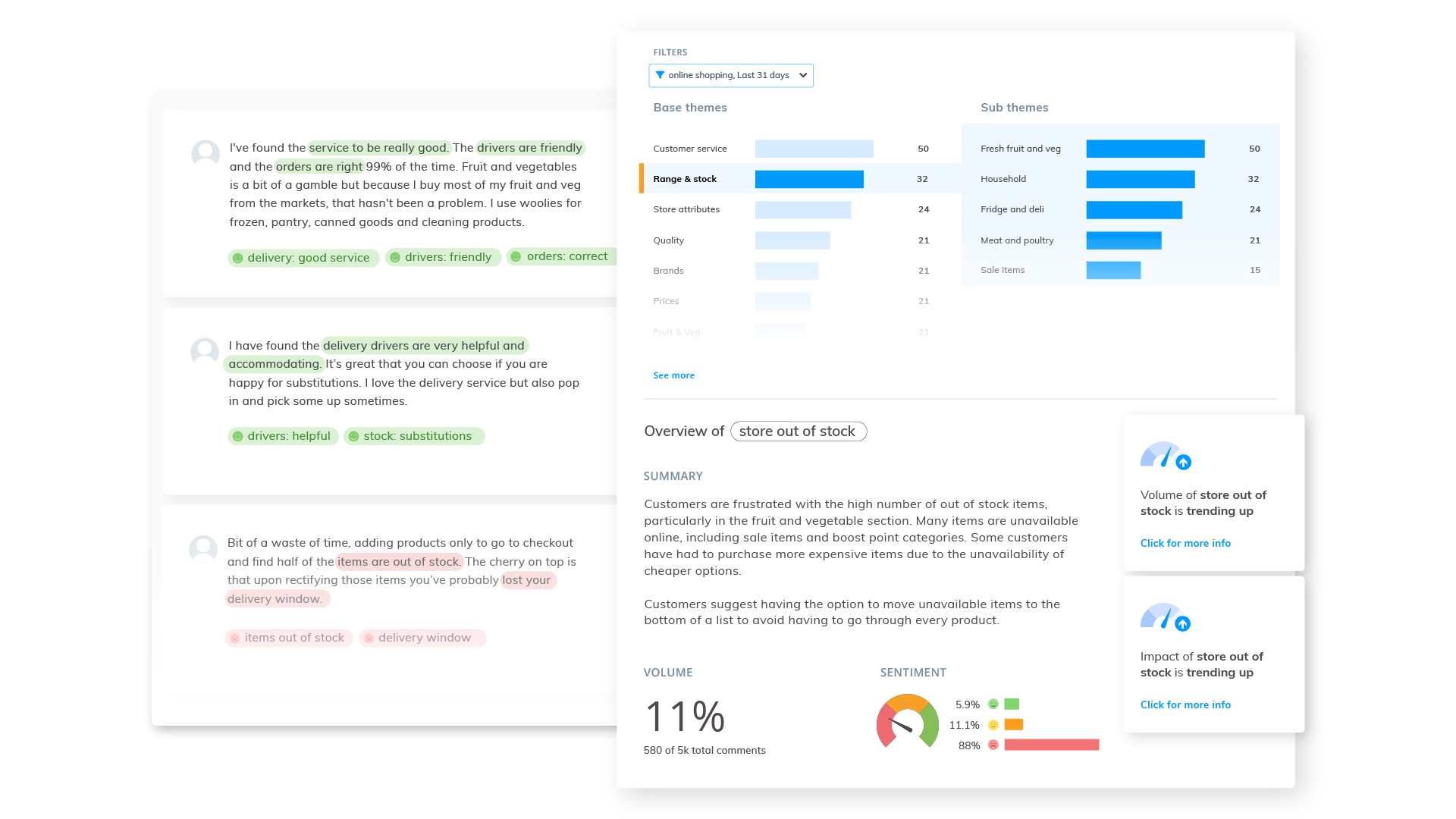
To better understand the practical applications of qualitative and quantitative data, let’s take a look at some real-world examples that demonstrate how these two types of data can be used in various fields.
Qualitative Data in Action
Some real world examples of qualitative data include:
- Analyzing interview transcripts to better understand customer preferences
- Analyzing responses to open-ended survey questions
- Observing customer behavior in a retail environment
- Assessing the impact of a new policy on a community
Qualitative data allows you to dig deeper into the reasons and motivations behind certain behaviors, providing valuable insights that can inform decision-making and guide future actions.
For instance, a product designer may conduct in-depth interviews with users to gain insights into their needs and preferences, helping them create a product that truly meets the needs of their target audience.
In the medical field, qualitative data can be used to assess patient satisfaction with a particular treatment or procedure. This data can then be used to inform decisions about how to improve patient care.
Customer experience professionals can analyze the qualitative data from support chat logs to identify common issues and requests. These can be quantified to enable the right actions - perhaps updating the company's FAQ page to guide customers, or prioritizing a bug fix.
Quantitative Data in Action
Quantitative data can be seen in action through:
- The use of surveys to measure customer satisfaction (although often these surveys will combine quantitative questions with qualitative open-enders)
- Analyzing sales data to identify trends.
- Comparing test scores between different educational programs.
This type of data provides objective, measurable information that can be easily compared and analyzed, allowing researchers to make informed decisions based on trends and patterns.
For example, a marketing team may use quantitative data to analyze the success of various advertising campaigns, identifying which strategies are most effective in driving sales and customer engagement.
By relying on measurable and objective data, you can make data-driven decisions and develop strategies that are grounded in evidence and proven results.
Summary
Understanding the differences between qualitative and quantitative data, as well as knowing when to use each type, is essential for conducting effective and well-rounded research.
While qualitative data provides depth and context, allowing you to explore the complexities of human experiences, quantitative data offers objective and measurable insights, enabling you to identify trends, relationships, and make predictions.
By combining the strengths of both types of data, you can develop a more comprehensive understanding of any research question, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
So, the next time you're working on a research or analysis project, remember to consider both qualitative and quantitative data. Aim for a well-rounded approach so you can uncover valuable insights and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of qualitative and quantitative data?
An example of qualitative and quantitative data could be measuring annual income (quantitative) and collecting occupation data (qualitative) to provide a more comprehensive understanding of average annual income for different occupations.
How do you know if the research is qualitative or quantitative?
You can tell if the research is qualitative or quantitative by looking at the type of data collected. Quantitative research focuses on numerical data and seeks to quantify a problem, while qualitative research focuses on non-numerical data and seeks to gain an in-depth understanding of a topic.
Examining the data type can provide clues as to the type of research being conducted.
What is an example of quantitative data?
Quantitative data is information that can be expressed in numerical values. An example of quantitative data could be height, weight or age. For instance, if you weigh 130lbs, that would be an example of quantitative data.
Another example would be if you are 25 years old; this is also an example of quantitative data.
What is the main difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
Qualitative data provides a richer understanding of a topic, while quantitative data is more focused on concrete facts and figures.
When should I use qualitative data in my research?
Qualitative data is best used to uncover why things happen and gain a deeper understanding of how people interact with and feel about certain topics. It can be particularly useful in understanding the motivations behind specific behaviors.
Stay up to date with the latest
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.