Thematic Analysis: An Overview + Guide
Explore how thematic analysis can help you uncover valuable insights from qualitative data. Compare manual and AI-driven methods, discover best practices, and see how Thematic software can streamline your analysis process.
Collecting customer feedback has never been easier. Studies show that 85% of people share feedback after a great experience, and 81% after a bad one. But raw feedback—whether from surveys, online reviews, or social media—contains much more than basic opinions. When analyzed correctly, it reveals deep insights that can transform business decisions and customer experiences.
To unlock these insights, companies rely on thematic analysis software. This powerful tool helps identify patterns and recurring themes within qualitative data, turning scattered feedback into actionable intelligence.
This guide will walk you through the thematic analysis process, key techniques, and best practices. Whether you're new to qualitative analysis or looking to refine your approach, these insights will help you maximize the value of your customer feedback.
Key Takeaways
- Thematic analysis turns qualitative data into insights – It helps identify key patterns in qualitative data like customer feedback, leading to smarter business decisions.
- AI speeds up analysis, but humans refine insights – AI automates theme detection, but human oversight ensures accuracy and real-world relevance.
- It’s useful across industries – From customer feedback to employee engagement, thematic analysis helps uncover valuable trends.
What is Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is a common qualitative research method that involves identifying and analyzing patterns or themes. It’s a way to organize large volumes of text-based information into a coding framework like groups or themes.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data in Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis works specifically on qualitative data which is descriptive and conceptual. You usually collect this type of data through open-ended surveys, interviews, focus groups, social media conversations, customer support conversations (conversational analytics), or customer reviews. Unlike quantitative data, which is numerical and easily measured statistically, qualitative data requires a more nuanced and multifaceted approach to interpretation and analysis.
What is a Theme in Thematic Analysis?
In thematic analysis, a “theme” is a recurring pattern of meaning. Themes come from codes, which are labels assigned to segments of text representing important ideas. They go beyond simple keywords, capturing broader concepts that summarize what people are saying or experiencing. For example, themes in product reviews might include “ease of use” or “value for money.” It's crucial that themes and codes are data relevant, meaning they should align with the entire data set and reflect the most critical information related to your research question.
Using themes to interpret qualitative data is an effective way of organizing similar pieces of information together. But, more importantly, themes help researchers and analysts identify the most common or predominant ideas within a dataset. When those themes are connected to a dataset of customer feedback, it means organizations can draw meaningful conclusions about what their customer need and want – and take targeted action.
Using Thematic Analysis: Common Use Cases
There are various scenarios where you might use thematic analysis. Thematic analysis is about identifying key themes or patterns in unstructured, text-based data, which is why the methodology lends itself well to customer feedback analysis. It can help you explore how your customers make sense of an issue or experience and, therefore, what you can do to solve the problem or improve the experience.
Here are some common use cases where thematic analysis proves particularly valuable:
Customer Feedback Analysis
With thematic analysis, you can analyze open-ended survey responses, customer reviews, support tickets, and social media conversations to identify recurring pain points, preferences, and areas for improvement. It can also help you consolidate customer feedback into actionable insights for building voice of the customer (VOC) programs, product development, and marketing strategies.
Market Research and Competitive Intelligence
How does your organization stack up against your competitors? You can use thematic analysis to monitor online conversations, discussions, and mentions of your brand to identify emerging trends, competitor strategies, and consumer sentiment.
Product Development and UX Research
Thematic analysis of user feedback and observations during usability testing can reveal crucial insights when developing software or hardware products. By identifying pain points, areas of confusion, or unmet needs, you can make targeted improvements to your designs and prioritize feature requests, enhancing user experience and overall product success.
Human Resources and Employee Engagement
Thematic analysis of open-ended survey responses and employee feedback can help HR teams identify how satisfied employees are in their jobs and what initiatives will help improve workplace culture and engagement. It’s also useful for analyzing exit interviews and identifying any recurring or underlying issues that might affect employee turnover.
Reflexive Thematic Analysis in Academic and Social Research
Thematic analysis is a cornerstone of qualitative research, enabling qualitative researchers to identify patterns and themes systematically, especially when interpreting findings from multiple studies.
Reflexive thematic analysis allows researchers flexibility to change, remove, and add codes throughout the analysis process. The coding process is crucial in manual thematic analysis as it helps in systematically categorizing and interpreting the data.
Addressing Specific Business Questions
You can derive business insights through thematic analysis to answer a variety of business questions, such as:
- What are the most common reasons for customer churn?
- What are the key features or functionalities that customers value most?
- What are the emerging trends and conversations in our industry?
- How do our competitors position themselves in the market?
- What are the main drivers of employee satisfaction or dissatisfaction?

A Practical Example of Thematic Analysis
Improving CX with Customer Feedback Analysis
Serato is a global audio software company that collects thousands of customer feedback responses through Zendesk. They found manually analyzing the data overwhelming and time-consuming and struggled to identify actionable insights.
Serato implemented Thematic's Zendesk integration to automate processing and interpreting their customer feedback data. Thematic's analysis helped identify specific product issues and get a granular understanding of customer sentiment. With this knowledge, the leadership team made data-driven decisions about product development and strategic partnerships.
The company also addressed specific product issues which created a better overall customer experience, improving loyalty and satisfaction. And, by automating the analysis process, Serato saved valuable time and resources, allowing them to scale their customer feedback analysis efforts as their user base grows.
How To Do A Thematic Analysis
Traditionally, thematic analysis has helped psychology, sociology, and other social science researchers and analysts understand people’s lived experiences, thoughts, and perceptions. The process has heavily relied on the time and effort of those expert researchers and analysts. But, as organizations gather more and more data, the need and desire to interpret what customers are saying and how they’re feeling has grown exponentially.
That’s where artificial intelligence offers a faster, more efficient alternative. AI-powered solutions leverage advanced algorithms and large language models (LLMs) to automate many of the manual steps of thematic analysis, uncovering hidden patterns and themes with speed and accuracy – particularly when dealing with large datasets. However, it’s still important to understand the steps of manual thematic analysis, because no matter what solution you use, human oversight will be required to validate the accuracy.
Let’s dig deeper into how to perform thematic analysis using the traditional (and manual) analysis method. For an in-depth look at automated thematic analysis, jump down to this section: How to Do A Thematic Analysis Using AI, LLMs & Generative AI.
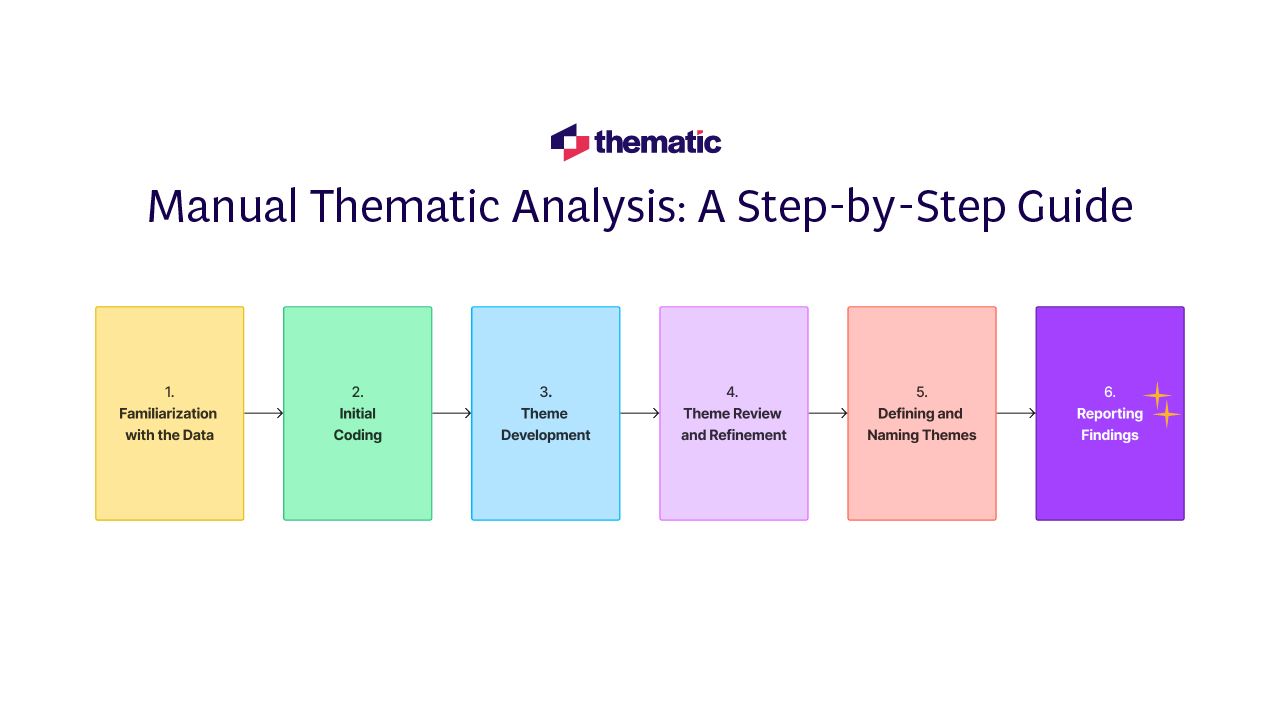
1. Get to know your data
This first step is where you get to know your research questions and data really well. It’s important to become familiar with the dataset so you can spot patterns or ideas. As you engage with the data, highlight key phrases, jot down initial thoughts, and ask questions.
2. Create and assign initial codes
As you read through your data, start highlighting key pieces of information that stand out or seem interesting. Otherwise known as labelling segments of text with codes – concise words or phrases that capture the essence of an idea or concept expressed – this process will help you break down the data into manageable chunks.
Use a consistent coding scheme and maintain a codebook to document your coding decisions. This ensures clarity and consistency throughout the analysis.
Start with a broad set of codes and refine them as you progress. Use a consistent coding scheme to ensure reliability.
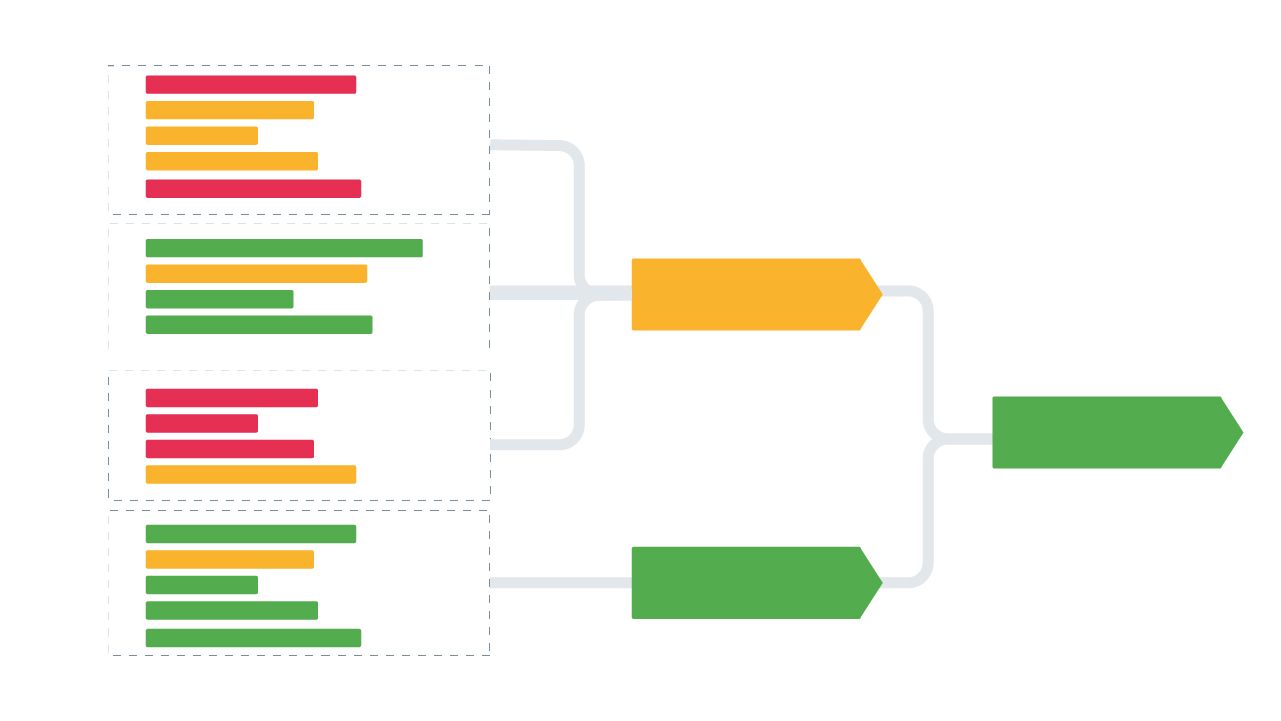
3. Start searching for themes
Now that you’ve coded your data, you can start grouping those codes into broader categories – or themes. This step is about condensing individual bits of data into a bigger, overarching idea or topic.
Use mind maps or concept maps to visualize the relationships between codes and themes.

4. Review and refine themes
At this point, you want to take a step back and review the themes you’ve created. Check if the themes you’ve identified connect to the data and you have evidence that supports or challenges your interpretations. Sometimes, themes need to be adjusted or combined so they accurately reflect what the data is telling you.
Maintain a codebook to document your coding decisions and theme definitions.
5. Define and name themes
Now that you have your themes, you can go into more detail about what each one means. Give each theme a clear and concise name and brief description. This will help you clarify the meaning of each theme, so you can easily explain and share your findings with others.
Use clear and concise language when defining and naming themes.
6. Report on your findings
Finally, its time to put everything together into a thematic analysis report. This includes presenting your themes, supporting them with examples from the data, and discussing what the themes mean in the context of your research. Incorporating visual elements like tables, charts, and diagrams will help you tell the story the data is telling.
Use a narrative approach to tell the story of your data through your themes.
Pros and Cons of Manual Thematic Analysis:
Why Its Best To Take An Inductive Approach In Thematic Analysis
When conducting thematic analysis manually, there are two primary approaches: inductive and deductive. These influence the thematic analysis process and how you interpret your findings.
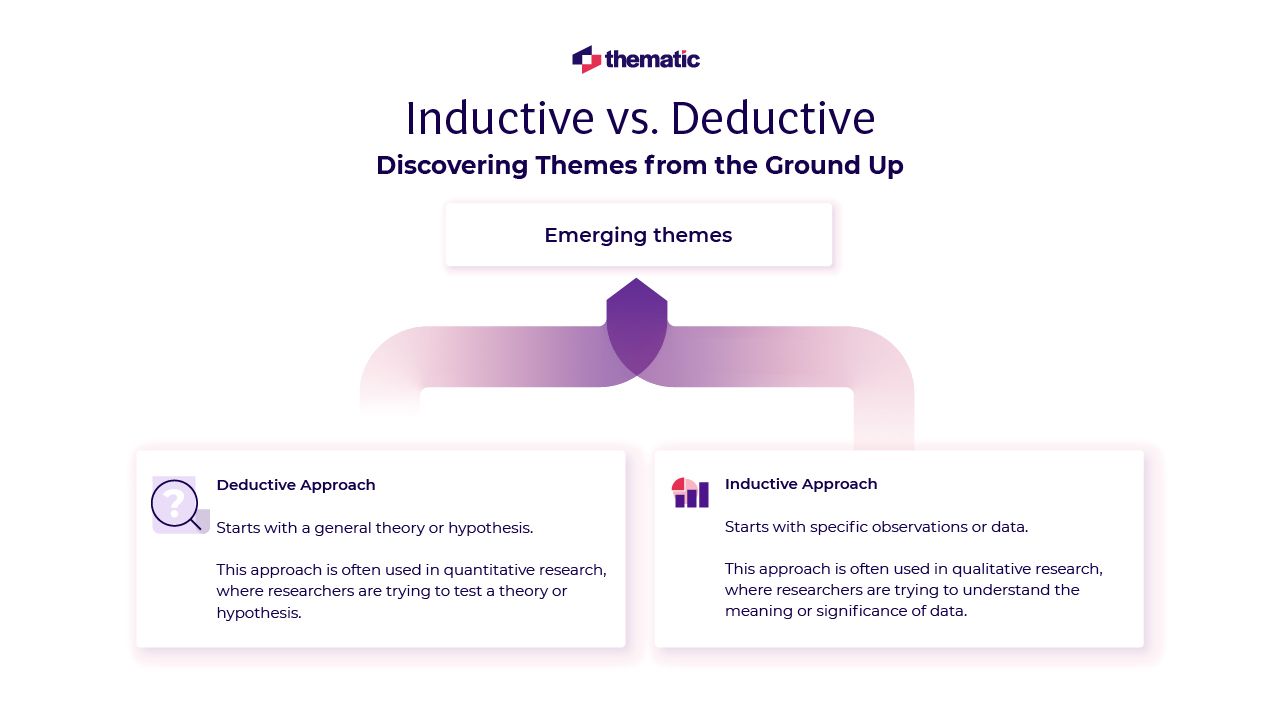
Many researchers choose to use an inductive approach because it lets you discover patterns or themes that emerge naturally from the data – or “from the ground up” – rather than forcing the data into pre-existing categories. Letting the data guide your analysis often results in richer, more authentic insights.
With a deductive approach, you begin with a set of ideas, theories, or specific themes, and use the data to confirm or challenge those them.
How To Do Thematic Analysis Using AI, LLMs & Generative AI
Now that you have an understanding on traditional thematic analysis, here’s how you can use advanced AI tools, LLM and Generative AI to speed up the process of identifying themes in qualitative data.
Whether you build your own AI-powered feedback analytics solution or buy a proprietary solution like Thematic, here’s how it works:
1. Bring your data together
This first step is where all your data from interviews, surveys, social media posts, and online reviews is consolidated into a single system. The goal is to organize everything in one place so it can be easily processed by AI.
You can do this by using a centralized data warehouse or by building connectors into various tools. In Thematic, you can import your data automatically from your different data sources, so you always have the most up-to-date feedback to analyze.
2. AI analyzes your data
After data integration, the AI engine analyzes your data. It identifies keywords, phrases, and concepts and categorizes them into potential themes. Generative AI can process and analyze much more data faster than a human can. It also isn’t prone to human bias or limited by time constraints like manual thematic analysis. Thematic's AI algorithms automatically identify and extract relevant themes from your data, saving you countless hours of manual coding.
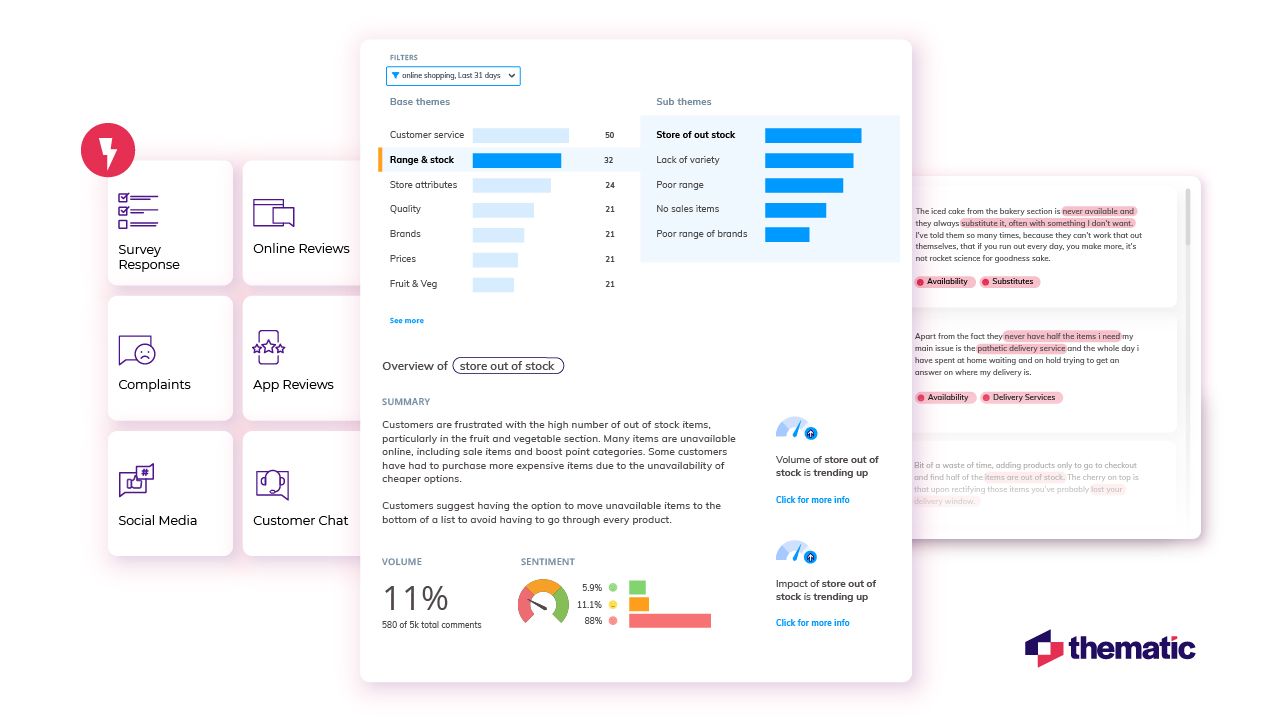
3. Simplify with theme visualization
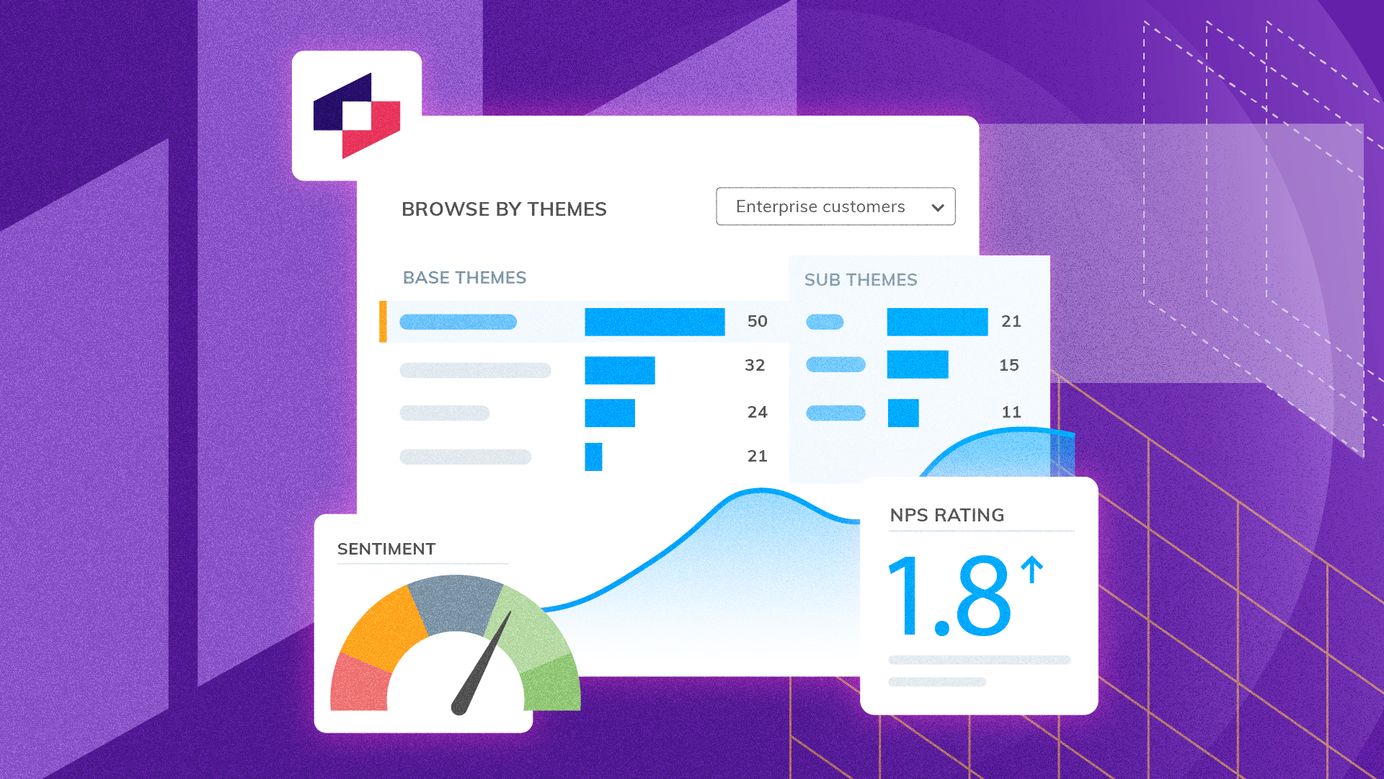
Once AI has identified potential themes, the next step is to visualize them in a way that’s easy for anyone to understand – this might involve charts, graphs, and word clouds that show how often certain themes or topics appear in the data. Thematic's intuitive visualizations and dashboards allow you to explore themes, track trends, and uncover hidden insights.
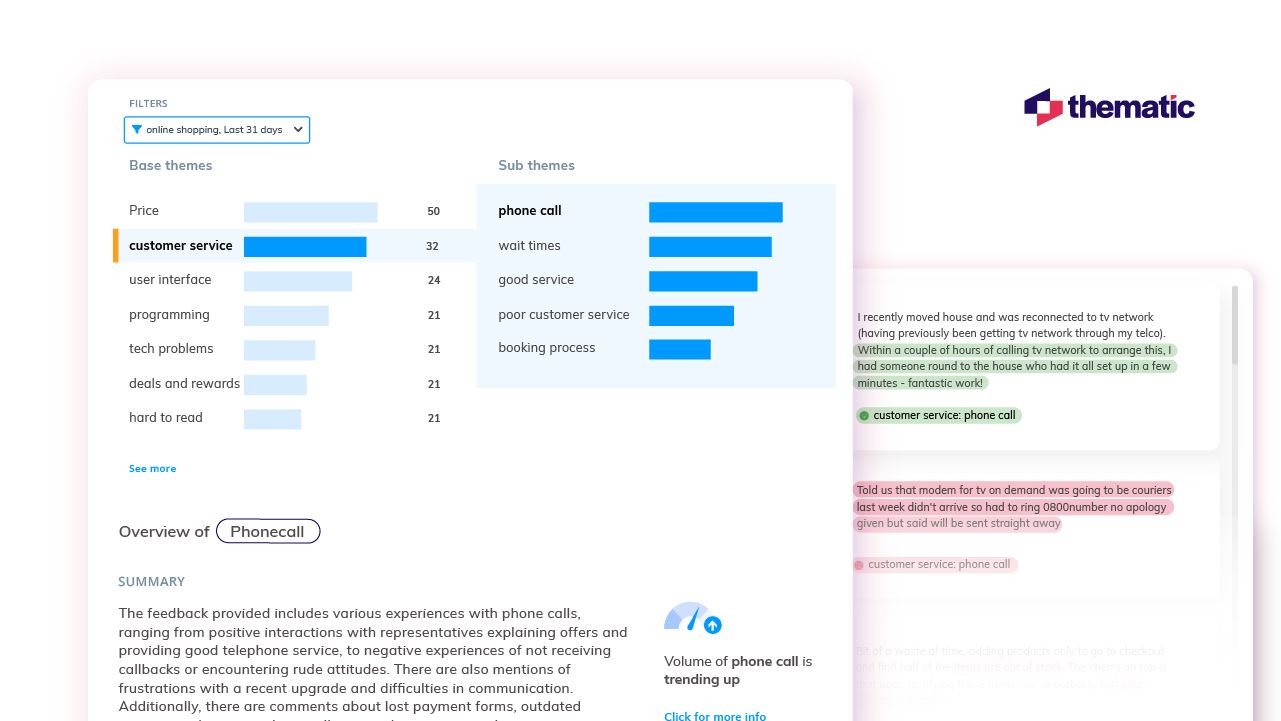
4. Explore themes
Now it’s time to dive deeper into the themes. This step is where you validate the findings, see if they make sense, and explore their meaning in greater detail. With Thematic, you can review and refine the themes the software automatically generates to ensure they align with your goals and objectives.
5. Actionable insights for data-driven decisions
With AI-powered thematic analysis solutions like Thematic, you can turn themes into concrete and actionable insights. This means you can make better business decisions based on real customer experiences, thoughts, and opinions. For example, if a common theme in customer feedback is "poor service," the actionable insight might be to invest in better staff training. You can also easily share your findings with stakeholders, colleagues, or clients through customizable reports and presentations.
AI-driven thematic analysis significantly improves efficiency, allowing analysts to process vast amounts of qualitative data much faster than manual methods. While AI tools like ChatGPT can support coding, summarizing, and organizing themes, human expertise remains essential for contextual interpretation. As a study in the Journal of Medical Internet Research highlights:
"ChatGPT can function as a valuable tool during analysis, enhancing the efficiency of thematic analysis and offering additional insights into qualitative data. While ChatGPT may not adequately capture the full context of each participant, it can serve as an additional member of the analysis team, contributing to researcher triangulation through knowledge building and sensemaking."
This reinforces the idea that AI should be seen as an assistive tool rather than a replacement for human-led thematic analysis. AI can efficiently surface patterns, but human researchers play a vital role in refining themes, verifying accuracy, and ensuring meaningful conclusions
The Advantages of AI-Driven Thematic Analysis
AI-powered thematic analysis is not just about saving time and resources. By automating the analysis process using AI, LLM, and Generative AI, you can gain a deeper, more nuanced understanding of your customers’ wants, needs, and pain points. With this understanding, you can plan and implement change geared toward increasing customer loyalty, engagement, and satisfaction.
While manual thematic analysis is still popular in some industries, using thematic analysis software tools is quickly becoming the preferred choice.
Here’s why:
- You can process large volumes of text data significantly faster than a human analyst.
- AI algorithms help reduce the risk of human error and bias.
- AI-powered tools are scalable, so you dont’ have to invest time or resources in training more people as your business (and its data) grows.
In many cases, a hybrid approach that combines AI-powered analysis with human refinement offers the best of both worlds. You can leverage AI to identify initial themes and patterns quickly, then use manual analysis to interpret those themes in greater depth.
Beyond NLP: How LLMs Transform Text Analytics
Is your Thematic Analysis solution still relying on B-Grade NLP? Discover how large language models are revolutionizing text analytics, offering deeper insights than traditional NLP approaches.
- Understand key NLP limitations and LLM advantages
- View real-world results of AI-driven text analytics
- Learn how self-learning AI eliminates manual updates
- Cut analysis time from weeks to minutes

How to perform a thematic analysis using ChatGPT
For small datasets, you can use ChatGPT to analyze your customer feedback.
To start, input the raw data or text-based content you want to analyze and ask ChatGPT to identify key themes or patterns in the data. For example, you might say, "ChatGPT, please review this transcript and identify recurring topics or themes related to 'workplace culture’.”
Once you have your initial themes, ask ChatGPT to refine them further, including organizing the themes into hierarchical structures and merging similar themes. You can also use ChatGPT to assist in coding the data by grouping specific excerpts of text under the identified themes.
However, while ChatGPT is good at identifying patterns, it can’t apply theoretical frameworks, account for cultural nuances, or engage in critical reflection about the data. This can be a big limitation, especially when you’re analyzing large amounts of data. That’s when using a tool like Thematic that uses Generative AI and LLMs can allow you to scale the volume and depth of your analysis.
Ready to revolutionize your thematic analysis workflow? Request a personalized demo or start your free trial of Thematic today and discover how AI can transform your data into actionable insights.

Qualitative Content Analysis vs. Thematic Analysis
Like thematic analysis, qualitative content analysis is another method for analyzing qualitative data and identifying patterns. While they have their similarities, understanding their differences will help you decide which approach is best for your research project.
The differences between content analysis and thematic analysis
Thematic analysis is all about identifying and analyzing patterns or "themes" within qualitative data. These themes are often broad ideas or concepts that emerge from the data (inductive) and can help you understand deeper meanings, experiences, or behaviors. This method is more about meaning and interpretation – what’s the story and sentiment sitting underneath the data.
On the other hand, qualitative content analysis focuses more on systematically organizing and categorizing what is being said and how many times, based on predetermined categories or codes (deductive). It tends to be more structured than thematic analysis, and sometimes involves quantitative elements. Content analysis provides a more organized and sometimes quantifiable summary of the data, which can also be used to make comparisons or identify trends.
An example of using content and thematic analysis
In some cases, combining qualitative content and thematic analysis can be beneficial. For example, you could use content analysis to identify the topics or concerns frequently mentioned in reviews about smartphones.
You might start by coding common words or phrases, like "battery life," "screen quality," and "price," then categorize those codes into broader topics like "features," "price," and "usability". This will tell you what aspects of your products customers care about most.
Then, you can use thematic analysis to delve deeper into the meaning and significance of those topics. You would search for themes, e.g. "battery life as a deal-breaker," or "screen quality affecting work performance”, then group them into broader themes that explain deeper emotions or concerns like "long-lasting battery as essential for productivity," or "price vs. quality". These themes help you understand the underlying attitudes or concerns that drive customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction with your product.
Comparative Table: Content Analysis vs. Thematic Analysis
Sentiment Analysis vs. Thematic Analysis
As we’ve discussed, thematic analysis focuses on identifying and interpreting patterns of meaning (themes) within qualitative data. It’s about identifying what people are talking about and why it's important to them. Here's a real-world example: in a set of customer reviews, you might find themes like "affordability," "ease of use," and "durability."
In comparison, sentiment analysis focuses on the emotional tone or attitude. It’s about identifying how people feel about those things – are they positive, negative, or neutral? In the same set of customer reviews, a positive review might say "I love this product," while a negative review could say "This product broke after one week."
In essence, thematic analysis provides context and meaning, while sentiment analysis adds the emotional layer. Specialized thematic analysis software can be particularly useful in efficiently identifying and categorizing these themes, especially in large datasets.
The benefits of sentiment and thematic analysis
While thematic analysis and sentiment analysis deliver useful results on their own, combining them gives you a richer and deeper understanding of your data.
Using the same smartphone example above, thematic and sentiment analysis together might tell you that people love the camera quality but hate the battery life. This means your product's greatest selling point is its camera. However, to increase customer satisfaction, you’ll need to address battery performance issues. Practically, this means you might decide to highlight the camera in marketing while planning a future upgrade for the battery.
What is Thematic Analysis or Qualitative Data Analysis Software?
Thematic analysis software makes it easier and faster to do thematic analysis, especially when dealing with large amounts of text. This means you can spend less time identifying and coding themes, and instead focus on analyzing the data – and using it to make things better for your customers. These tools also help you visually map out themes and connections, which can make it easier to share research and insights across the wider organization.
Here are some popular thematic analysis or qualitative data analysis tools – and the features they’re most well-known for:
Thematic
Analyze customer feedback in real-time with Thematic and take immediate, impactful action. Thematic’s Generative AI not only enhances the quality and depth of insights, but it can also handle exponentially more data than human teams. So, as your datasets scale, you spend the same (not more) time analyzing it.
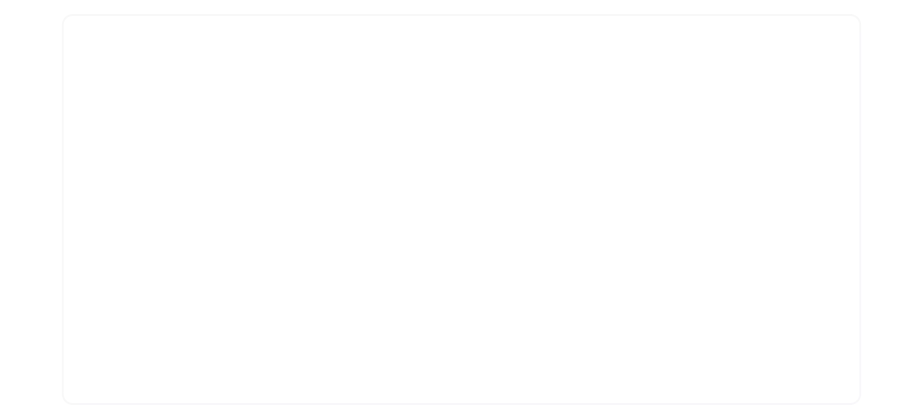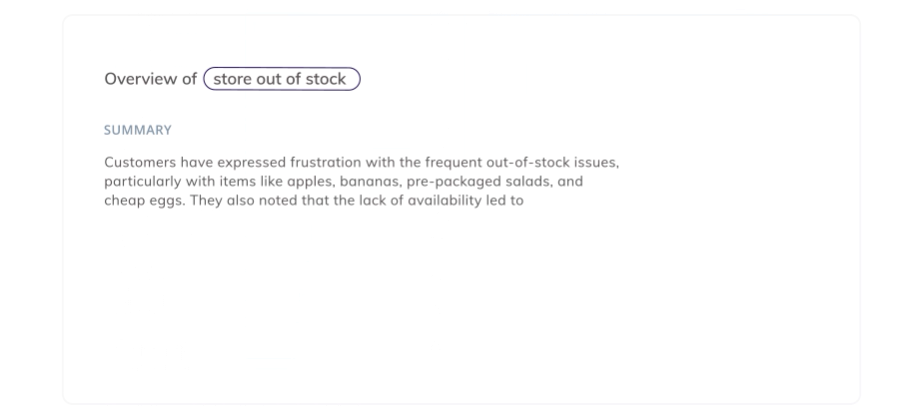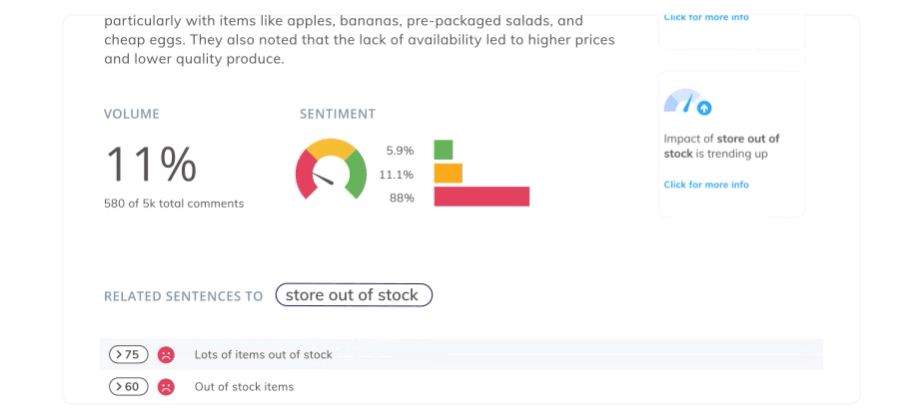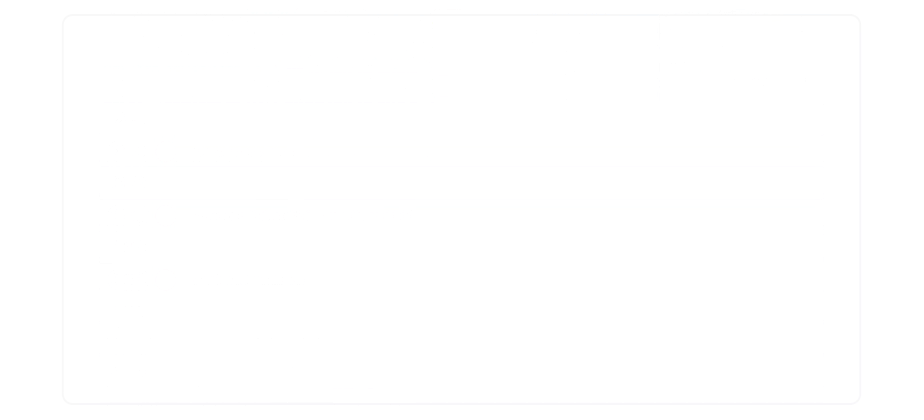
Thematic
AI-powered software to transform qualitative data into powerful insights that drive decision making.
Dovetail
Dovetail is a user research platform that’s best for small, one-off US research studies. With thematic analysis as one of its key features, you can easily analyze text and organize themes.
Relative Insight
Relative Insight uses NLPs and comparative analytics to identify themes and trends across data. It can be a useful tool for businesses with the goals of refining their messaging or improving customer engagement.
XM Discover
XM Discover by Qualtrics is an integrated platform with survey design, data collection, thematic analysis and reporting features.
MAXQDA
MAXQDA is a qualitative data analysis tool for qualitative and quantitative research. It has advanced coding capabilities which help facilitate deeper understanding of complex data sets.

CAQDAS vs. Thematic Analysis Software Tools
There are two main types of thematic analysis software: computer-assisted qualitative data analysis tools (CAQDAS) and thematic analysis software. While they can both help streamline and automate thematic analysis, CAQDAS tools don’t usually incorporate AI to automate the analysis process. This means that careful human interpretation and manual analysis are still components your team or organization will need to perform.
Do More, Be Better With Thematic Analysis and Insights
The ultimate goal of thematic analysis is empowerment. To tap into a wellspring of actionable insights that inform data-driven decisions, and ultimately, drive meaningful impact in your research, business, or organization. You can leverage thematic analysis to prioritize product improvements, refine marketing strategies, personalize customer interactions – and ultimately enhance your overall customer experience.
Ready to embark on your thematic analysis journey? You can try thematic analysis using your data with a free guided demo of Thematic.
Learn more about thematic analysis and AI tools
You can find out more about analyzing customer feedback and qualitative analysis in these guides:
- How to code qualitative data
- How to code and analyze open-ended questions
- Guide to thematic analysis software
- How to analyze customer and product reviews
- How to analyze survey data
We also have some free feedback tools and resources that may help you:
- Feedback collector (browser extension)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How is thematic analysis different from other research methods?
Thematic analysis focuses on finding patterns and meaning in qualitative data, like survey responses or customer reviews. Unlike content analysis, which counts how often words appear, thematic analysis digs deeper to understand what people are actually saying. And while grounded theory builds new theories from data, thematic analysis is more flexible—great for exploring existing ideas or customer feedback.
2. Can I use thematic analysis for small datasets?
Absolutely! Even if you only have a handful of interviews or a few survey responses, thematic analysis can still uncover valuable insights. The key is focusing on depth rather than numbers. If you’re working with a larger dataset, AI-powered tools like Thematic can help speed up the process.
3. What are the biggest challenges in thematic analysis?
Bias, inconsistency, and deciding what really matters are the main challenges. Since humans categorize themes, personal bias can creep in. Coding can also be inconsistent, especially when multiple people analyze the same data. Plus, it’s easy to get overwhelmed—which themes are actually important? That’s where AI-powered analysis can help by reducing bias and automating theme identification.
4. How can AI Improve thematic analysis without replacing human judgment?
AI makes thematic analysis faster and more scalable—it can process thousands of survey responses in minutes. But human expertise is still essential to interpret the findings, fine-tune themes, and add real-world context. The best approach? Let AI do the heavy lifting, then use human insights to validate and refine the results.
Stay up to date with the latest
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.