Thematic Analysis Examples In Action
Want to understand the "why" behind your customers' behavior? Our comprehensive guide on thematic analysis is here to help! Learn how to unlock hidden insights and drive your business forward with practical examples and actionable tips.
In today's data-driven world, understanding your customers is essential. Analyzing qualitative data through thematic analysis is a powerful tool that can unlock hidden meanings and reveal the "why" behind customer behavior.
This understanding is crucial, as CX-focused companies can command an additional 16% premium on the pricing of their products and services. Thematic analysis can help you unlock thee valuable insights needed to align with your customers' expectations and elevate their experiences.
This comprehensive guide will demystify thematic analysis, providing practical examples and actionable tips to harness the power of this methodology. Whether you're a seasoned researcher or new to qualitative analysis, you'll learn how to uncover valuable insights that can drive your business forward.
What is Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is a method used to identify, analyze, and report patterns (themes) within qualitative data. Thematic analysis involves a deeper understanding of the meaning and significance behind the data. The thematic analysis process includes recognizing codes and themes within a dataset, reviewing, finalizing, and reporting on themes, often using metaphors to illustrate the sorting of themes to identify patterns and overarching themes.
How Thematic Analysis Drives Meaningful Insights
Thematic analysis goes beyond surface-level observations to uncover the underlying meaning and significance of qualitative data. Data interpretation plays a crucial role in thematic analysis, as it helps in making sense of the identified patterns and themes. By identifying recurring patterns and themes, researchers and analysts can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence behavior, attitudes, and decision-making.
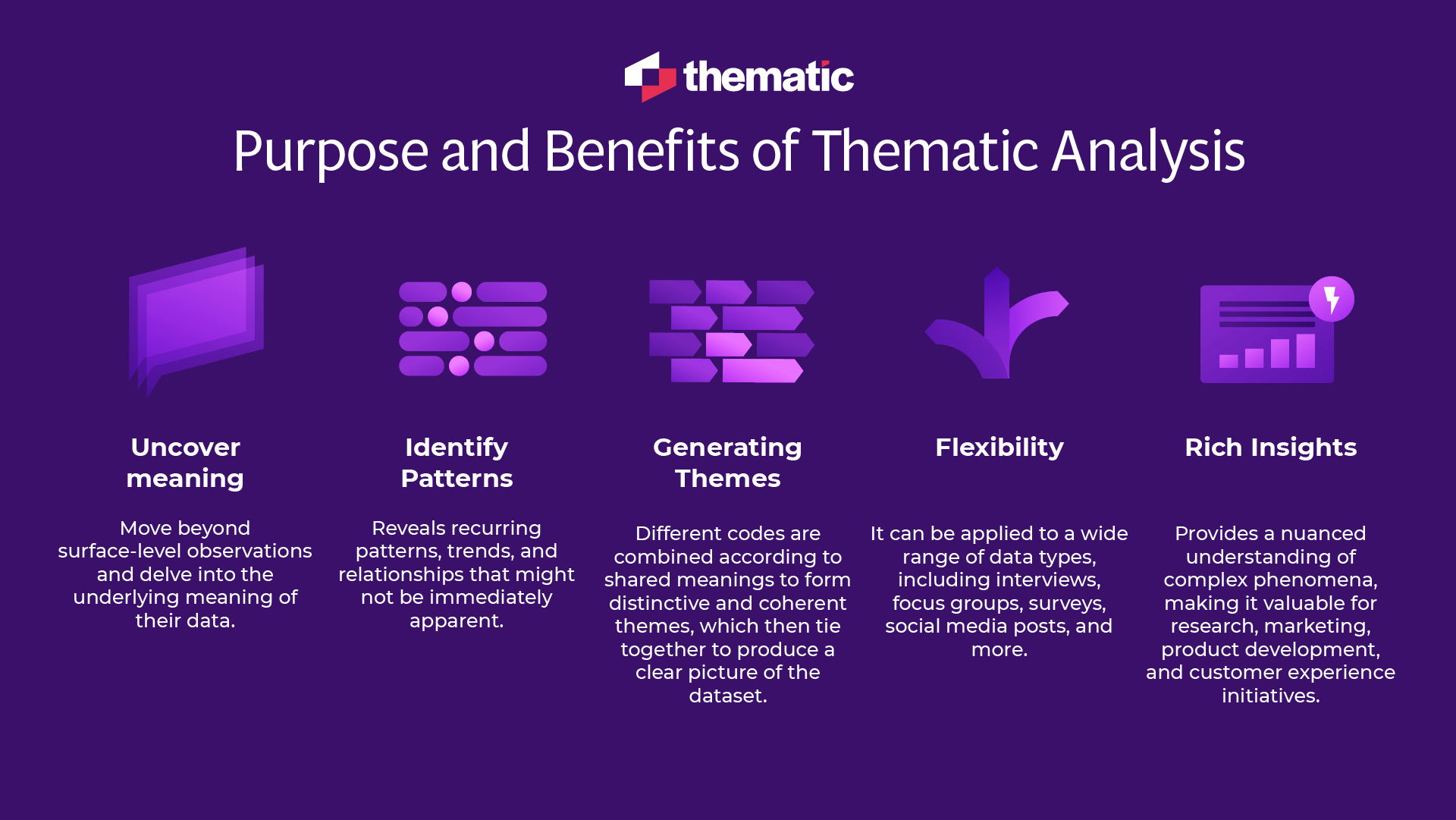
Purpose and Benefits of Thematic Analysis
- Uncover Meaning: Thematic analysis helps researchers move beyond surface-level observations and delve into the underlying meaning of their data.
- Identify Patterns: By systematically examining data, thematic analysis reveals recurring patterns, trends, and relationships that might not be immediately apparent. This process generates data-driven insights that are crucial for understanding the deeper implications of the data.
- Generating Themes: This involves analyzing and interpreting aggregated data to identify and develop meaningful themes or sub-themes. Different codes are combined according to shared meanings to form distinctive and coherent themes, which then tie together to produce a clear picture of the dataset.
- Flexibility: It can be applied to a wide range of data types, including interviews, focus groups, surveys, social media posts, and more.
- Rich Insights: Thematic analysis provides a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena, making it valuable for research, marketing, product development, and customer experience initiatives.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Data Analysis
Thematic analysis is specifically designed for qualitative data (non-numerical and descriptive), such as interviews and open-ended responses. This is in contrast to quantitative data (numerical), which is better suited for statistical analysis.
Tip: To learn more about the differences between these data types, you can read our article on qualitative vs. quantitative data.
Approaches to Manual Thematic Analysis
When conducting thematic analysis manually, researchers can choose between two primary approaches: inductive and deductive.
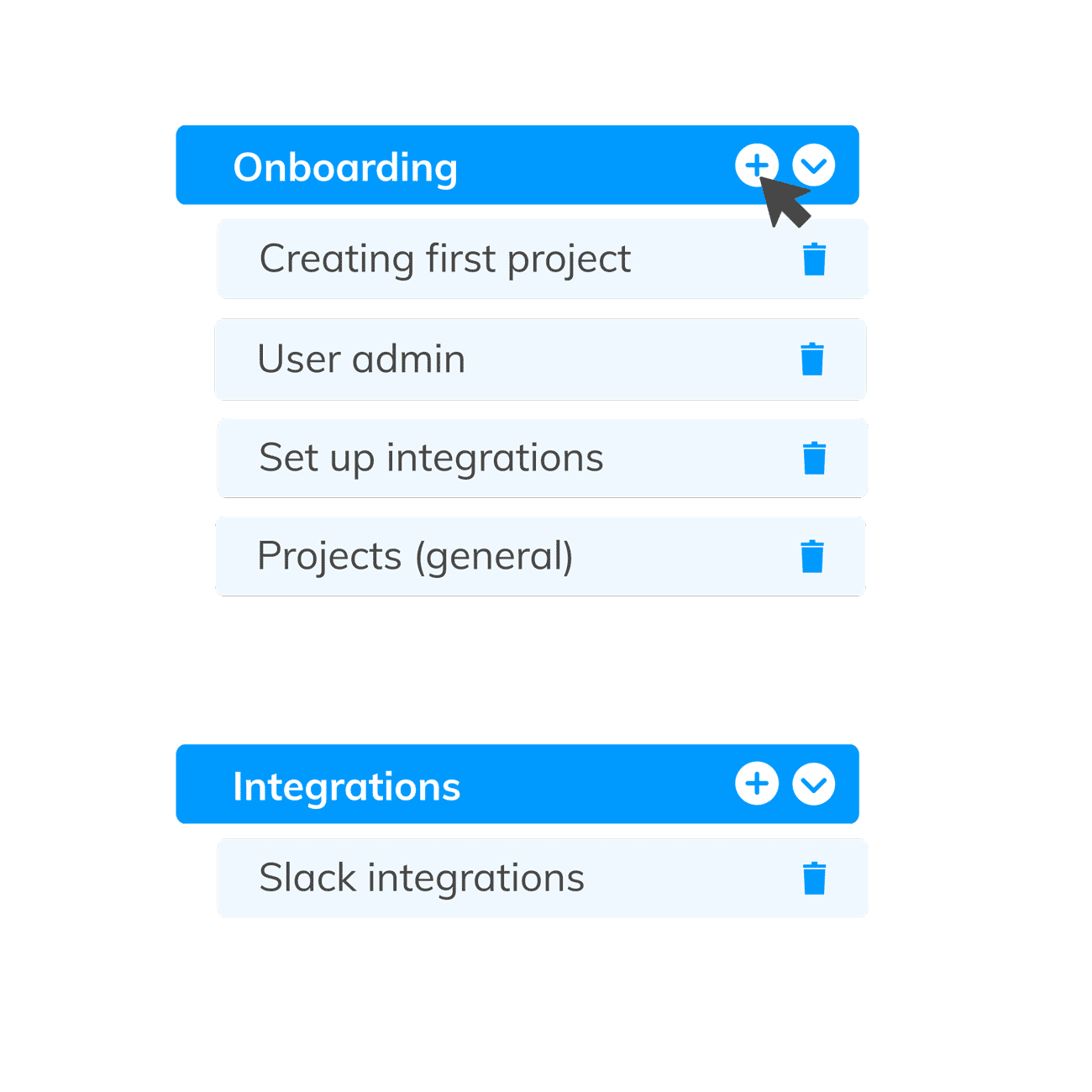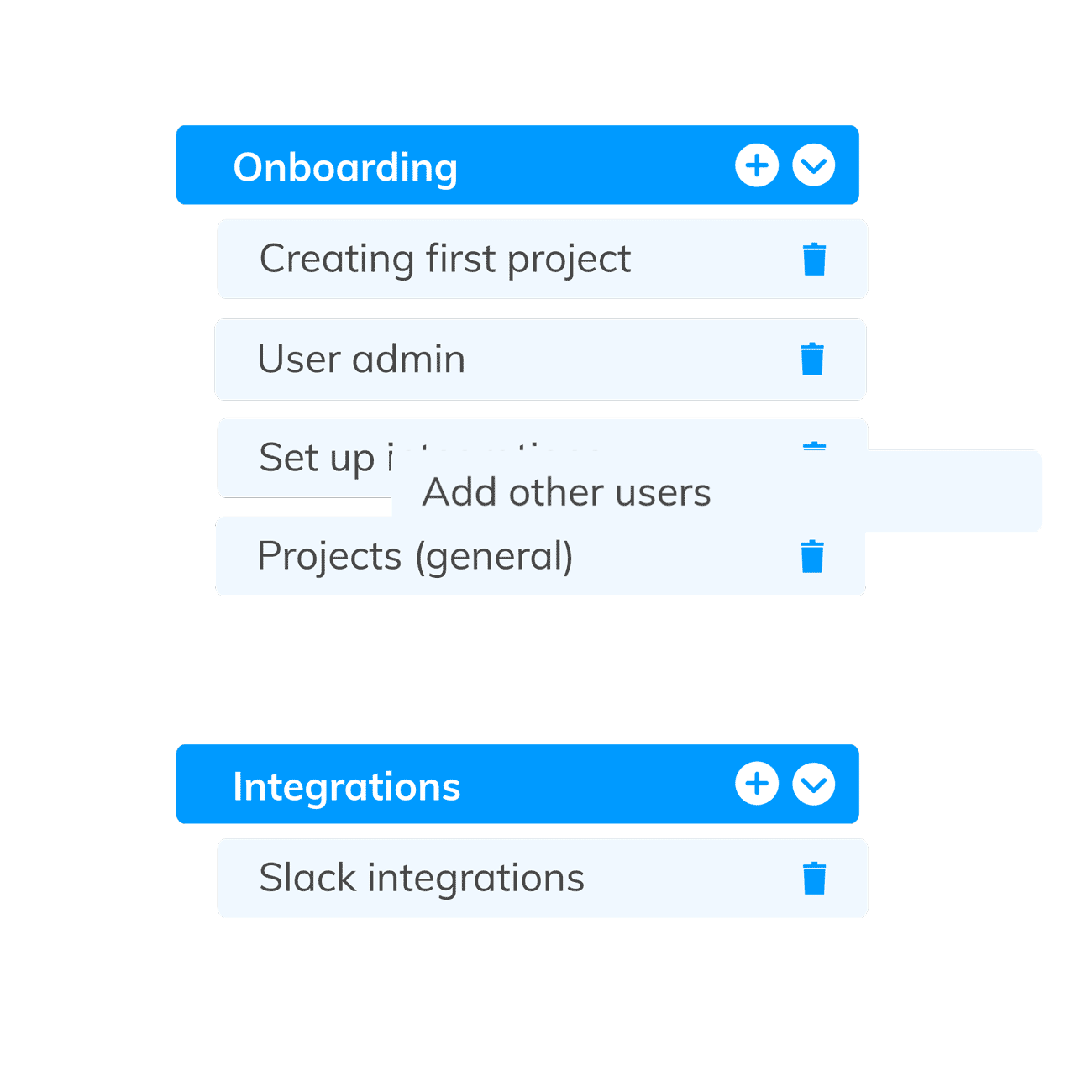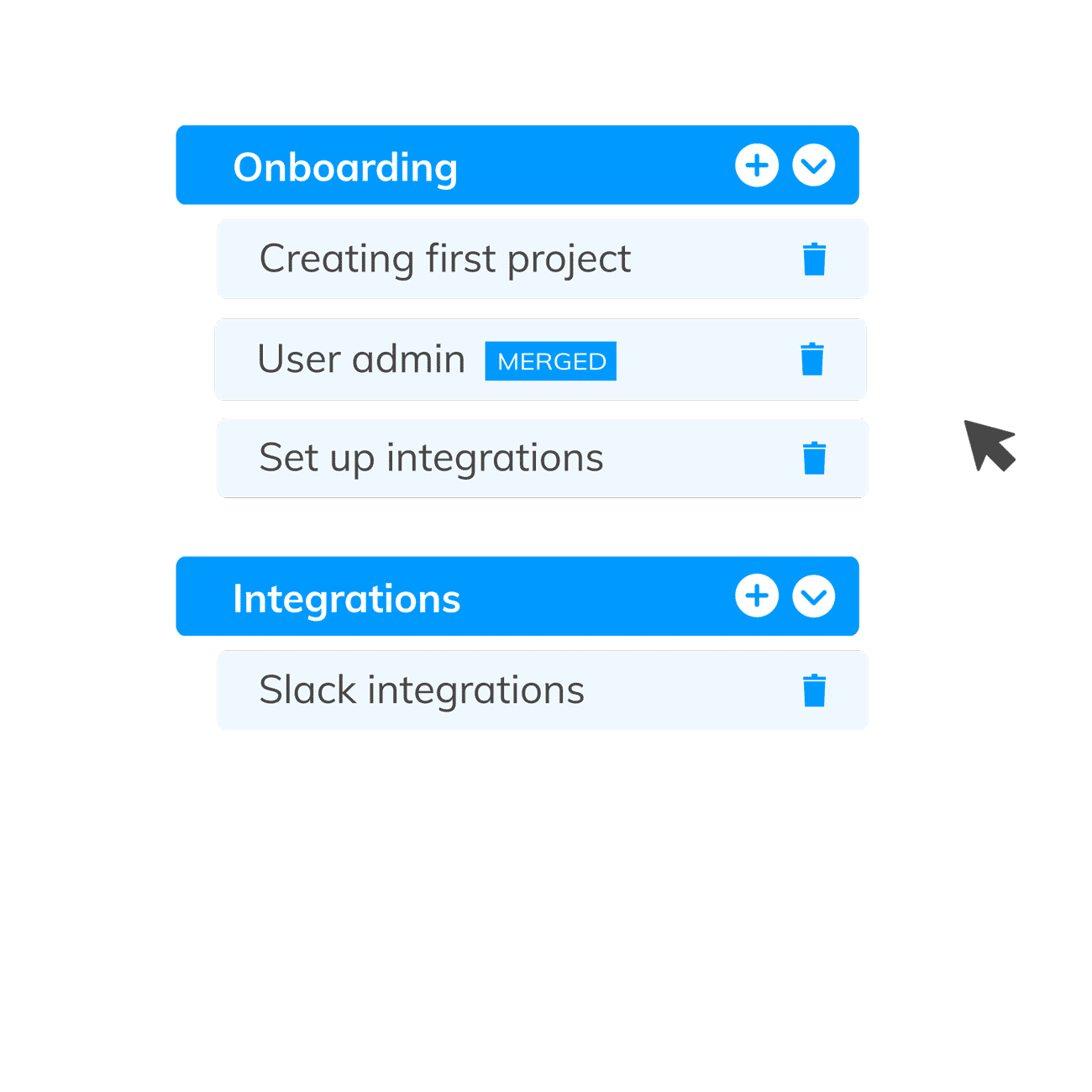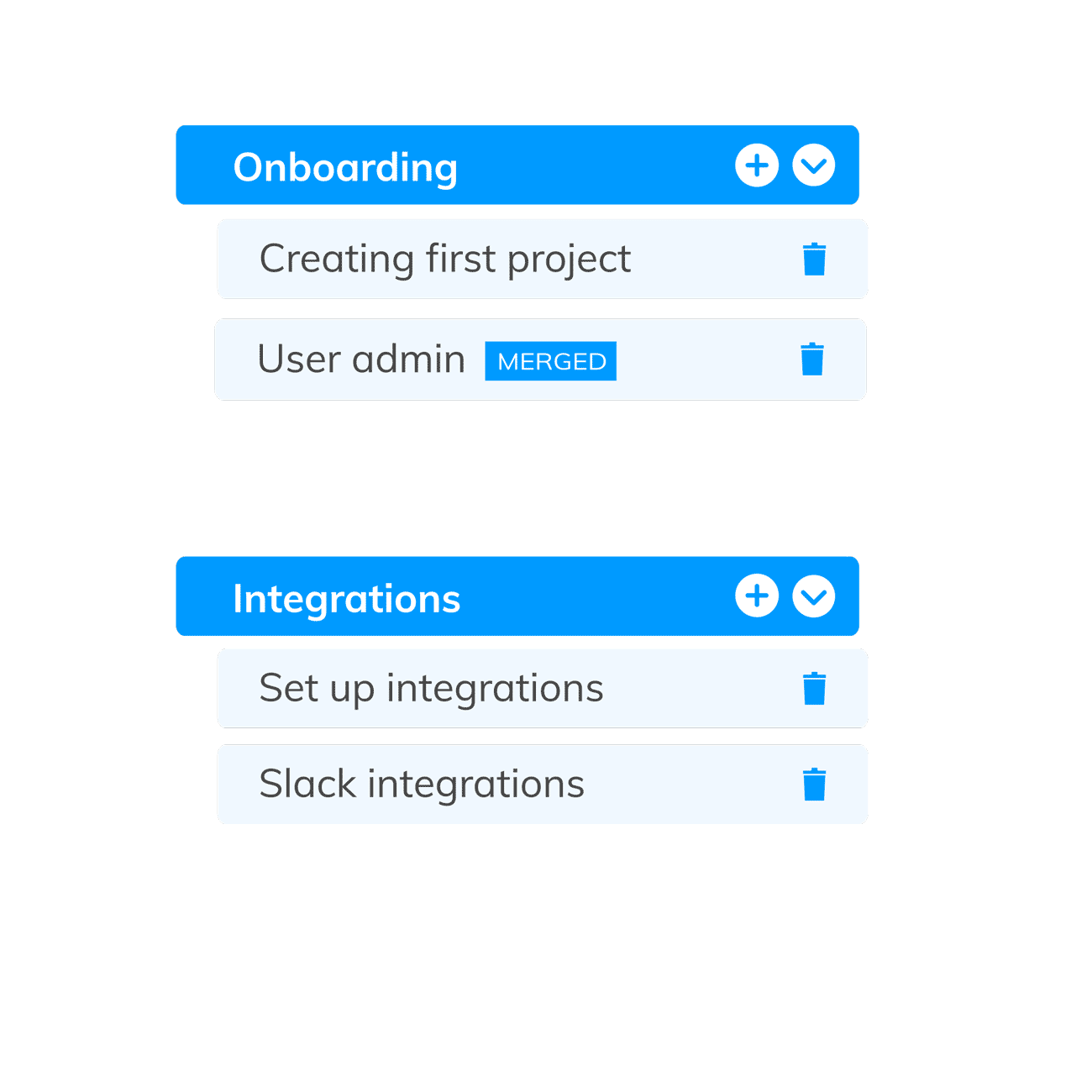
A thematic map is a tool used in thematic analysis to organize and visualize themes, helping researchers to see patterns and relationships within the data.
Data coding is crucial in thematic analysis as it involves using codes to categorize and describe the content of the data, which enhances the reliability and systematic nature of the analysis.
Inductive Approach
This bottom-up approach involves immersing yourself in the data without preconceived notions. Pattern recognition is crucial in this inductive approach as it helps identify recurring themes and trends within the data. Themes organically emerge from the data itself as you read, re-read, and analyze it. This approach is flexible and allows for unexpected findings, making it ideal for exploratory research where you’re seeking to discover new insights.
Deductive Approach
In contrast, the deductive approach is top-down. A theoretical framework plays a crucial role in this approach as it guides the selection of predetermined themes or codes. You begin with a set of predetermined themes or codes based on existing theories, frameworks, or research questions. You then systematically analyze the data to see if and how these themes are reflected. This approach is more focused and hypothesis-driven, making it suitable for research where you have specific expectations or want to test existing theories.

Thematic is an AI-Powered Thematic Analysis software that combines the best of both human & AI analysis. The themes editor is a tool that allows human users to access and make edits to the themes & codes created by our AI, ensuring the highest level of accuracy.
Choosing the Right Approach and Type for qualitative research
The choice between inductive and deductive approaches depends on your research question and the existing knowledge in your field. If you’re exploring a new topic, an inductive approach might be more appropriate. If you have specific hypotheses to test, a deductive approach might be more suitable.
Understanding the research methodology is crucial in thematic analysis as it guides the selection of appropriate methods and tools for data collection and analysis.
Similarly, the type of thematic analysis you choose will depend on your research goals and resources. If you’re working with a large dataset, automated analysis might be the most efficient option. If you need to ensure high levels of rigor and validity, coding reliability analysis might be necessary.
5 Ways Thematic Analysis is Transforming Industries: Real-World Examples
Thematic analysis isn't just a research buzzword. It's a powerful tool being used across industries to unlock valuable insights from qualitative data. Here are five examples showcasing how thematic analysis is making a real-world impact.
1. Academic Research: Improving the Learning Environment for Students
Consider a university starting a fresh online learning platform. They are curious about student adaptation, what is working and what has to be improved. Using thematic analysis and open-ended survey responses, they can find themes such "instructor support" and "ease of use." Equipped with this information, the university can implement focused enhancements meant to increase student happiness and learning results.
2. Market Research: Decoding Consumer Desires
A sustainable fashion brand is interested in understanding about what makes their customers tick. They employ two ways to get qualitative feedback: focus groups and social media content analysis. Using thematic analysis, they can identify important concerns such as "quality" and "environmental consciousness". Because of this information, they are able to tailor their marketing language and product offerings, resulting in higher sales and customer loyalty.
3. Healthcare: Understanding the Patient Journey
Researchers are learning how people manage persistent pain. Patient in-depth interviews expose themes including "self-care practices" and "social support." Apart from clarifying the patient experience, themed analysis promotes the creation of more successful pain control strategies.
4. Customer Feedback Analysis: DoorDash Delivers on Insights
Customers had a lot of things to say about DoorDash. It would be a logistical nightmare to evaluate everything by hand. By automatically identifying themes with the help of Thematic, they identified key themes such as "late deliveries" and "incorrect orders". DoorDash is able to enhance customer happiness and promptly handle any issues that may arise.
5. Human Resources: Building a Happier Workplace
A business that is having trouble retaining employees interprets the results of departure interviews by using thematic analysis. "Lack of career growth" and "poor management communication" are examples of recurring themes. The organization can use this information to make adjustments that will create a more pleasant and interesting work environment for everyone.
Manual vs. AI Thematic Analysis: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Examples of How to Report on Your Thematic Analysis
Effectively communicating the findings of your thematic analysis is crucial for making an impact. Here are common methodologies and visuals used for reporting:
- Narrative Reports: These reports provide a detailed, written account of the identified themes, their significance, and supporting evidence from the data. They often include quotes or excerpts to illustrate the themes.
- Visualizations: Visual aids like charts, graphs, and diagrams can help to summarize and communicate complex findings in a more accessible way. Data visualization plays a crucial role in reporting thematic analysis findings by making the data more understandable and engaging for the audience.
- Matrices and Tables: These can be used to organize and present themes, sub-themes, and associated data in a structured format.
- Presentations: Slideshows or presentations can be an effective way to share findings with stakeholders, especially when combined with visuals and interactive elements.
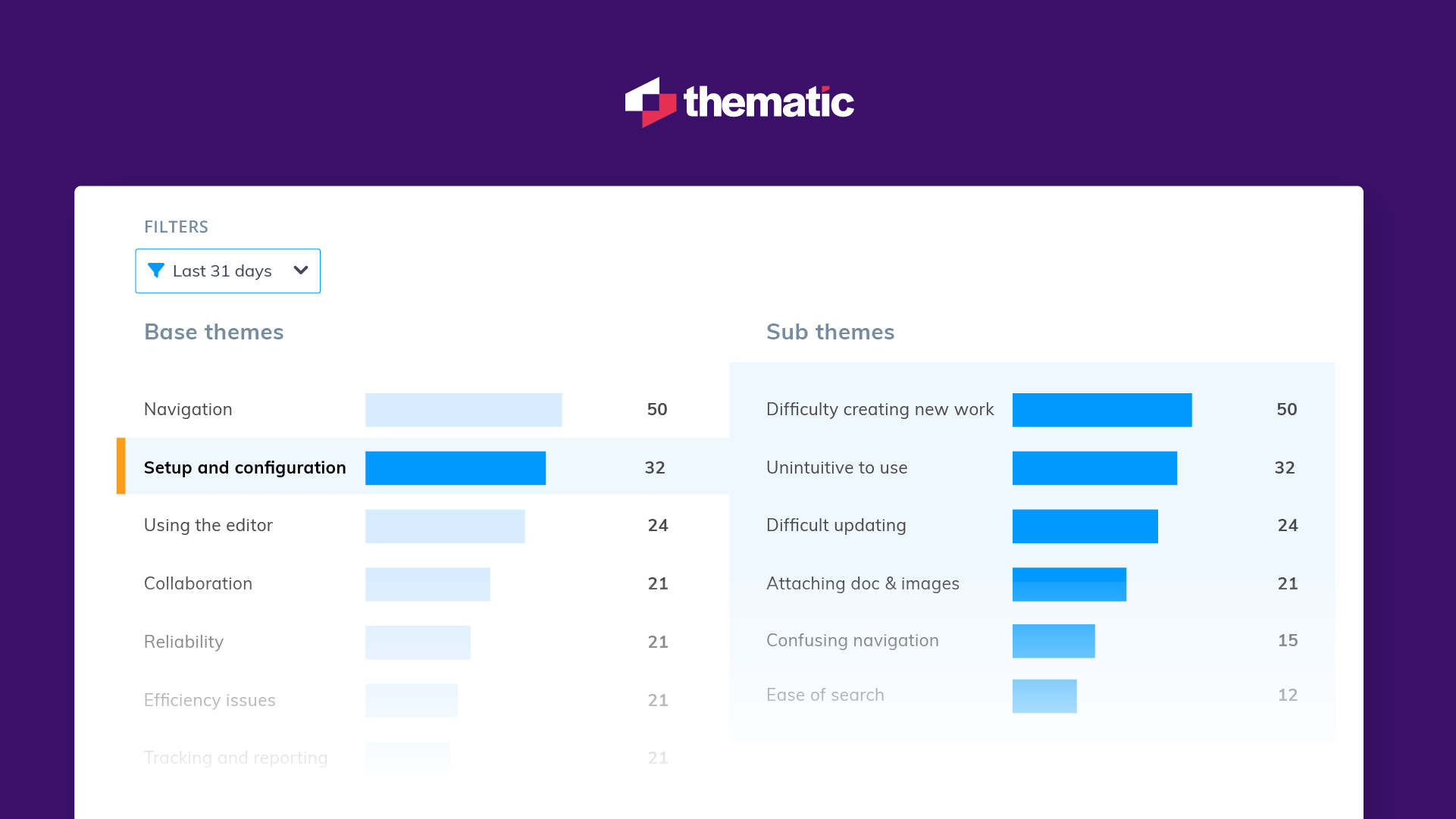
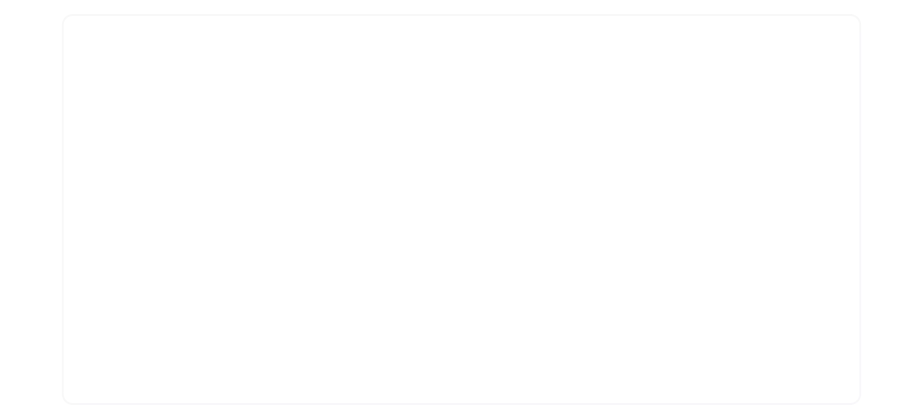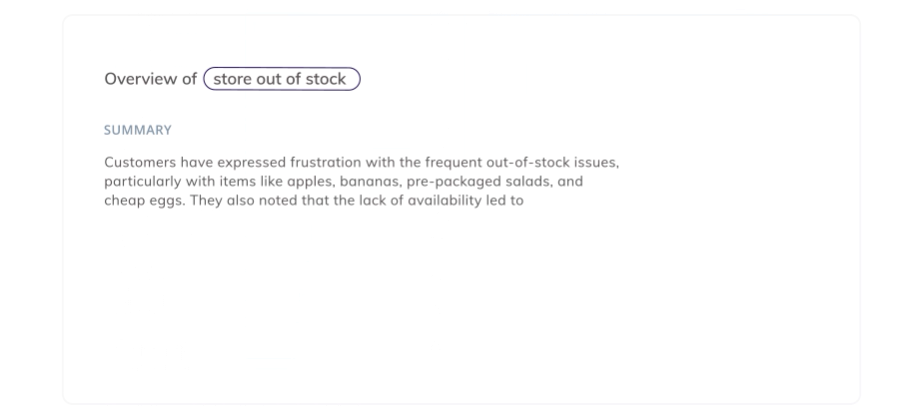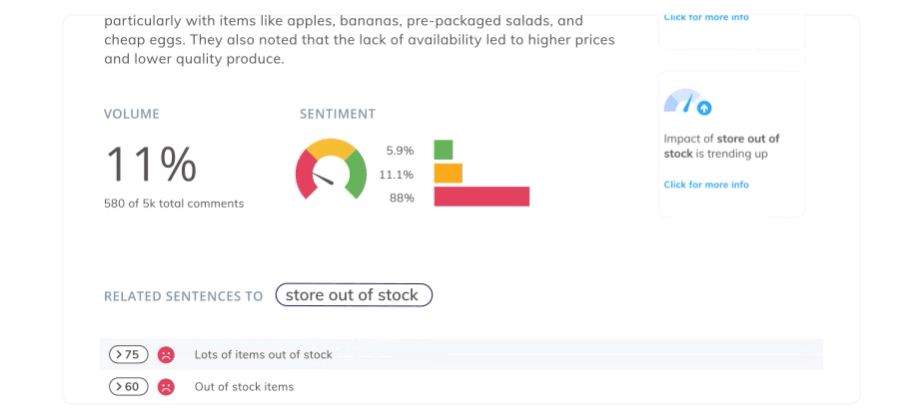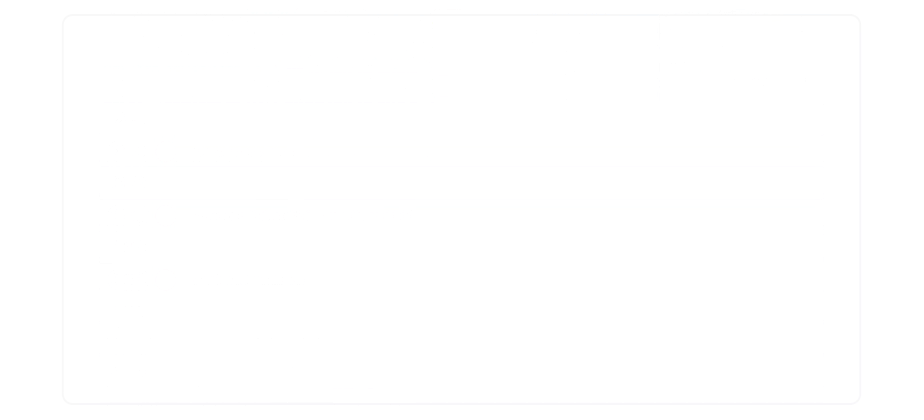
Example of the Visualization and Reporting Capabilities of an AI Thematic Analysis Software
AI-powered thematic analysis software often includes visualization and reporting features. For example, Thematic's platform automatically generates visually appealing and easy-to-understand reports showcasing identified themes, their frequency, sentiment, and co-occurrence. These reports can be easily customized and shared with stakeholders, simplifying the communication of complex insights and driving data-informed decision-making. These reports can be easily customized and shared with stakeholders, making it simple to communicate complex insights and drive data-informed decision-making.
Some of Thematic’s key reporting features include:
- Interactive Dashboards: Explore your data through interactive visualizations that allow you to drill down into specific themes and uncover deeper insights.
- Customizable Reports: Tailor your reports to focus on the most relevant themes and metrics for your audience.
- Shareable Insights: Easily share your findings with colleagues and stakeholders through exportable reports and presentations.
- Sentiment Analysis: Understand the emotional tone behind customer feedback to gauge overall satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
By leveraging Thematic’s powerful reporting capabilities, you can transform raw qualitative data into actionable insights that drive meaningful change in your organization.
7 Tips for Conducting Thematic Analysis
1. Immerse Yourself in the Data
Before diving into coding or theme identification, thoroughly familiarize yourself with your dataset. Data familiarization is crucial in the immersion process as it helps you understand the dataset's structure and content deeply. Read and re-read the data multiple times, paying close attention to the language used, the tone of responses, and the overall context in which the data was collected.
The immersion process allows you to gain a deep understanding of the nuances within the data, identify recurring patterns, and generate initial ideas for potential themes.
2. Develop a Coding Framework
Whether you’re using an inductive or deductive approach, having a clear coding framework is essential. This framework serves as a structured guide for your analysis, helping you organize your thoughts, maintain consistency, and ensure you capture all relevant aspects of the data.
AI-powered thematic analysis platforms like Thematic automate the coding framework process, eliminating the need for manual labor. Thematic's AI automatically identifies potential codes and themes, saving researchers valuable time and effort.
3. Be Flexible and Iterative
Thematic analysis is not a linear process; it’s an iterative one. Iterative coding is crucial in this process as it allows for continuous refinement and deeper understanding of the data. As you delve deeper into the data, you may discover new themes or realize that your initial codes need refinement.
Don’t hesitate to revise your coding framework and revisit previously coded sections as your understanding of the data evolves. Thematic's platform allows for "human-in-the-loop" interaction, enabling researchers to easily edit and refine the AI-generated coding framework to ensure accuracy and alignment with their research goals.
Thematic
AI-powered thematic analysis software to transform qualitative data into actionable business & CX insights
4. Look for Connections and Relationships
Themes rarely exist in isolation. Theme interrelation is crucial in thematic analysis as it helps in understanding how different themes connect and influence each other. As you identify themes, explore the connections and relationships between them.
- Are there overarching themes that encompass several sub-themes?
- Do certain themes contradict or complement each other?
Understanding these relationships will enrich your analysis and provide a more nuanced interpretation of the data.
5. Consider the Context
Always consider the broader context in which your data was collected. Contextual analysis plays a crucial role in thematic analysis by helping to understand the underlying factors influencing the data.
- Who were the participants?
- What were their backgrounds and experiences?
- What was the social, cultural, or historical context of the data collection?
Understanding the context can help you interpret the meaning behind the themes and avoid misinterpretations.
6. Use Software Wisely
Software tools like Thematic can be invaluable for streamlining the analysis process, especially with large datasets. Data automation plays a crucial role in the thematic analysis process by automating repetitive tasks, thus saving time and reducing human error. However, they should not replace human judgment and interpretation.
Use software to automate tasks like coding and theme identification, but always review and refine the results manually to ensure accuracy and capture the subtleties of the data.
7. Validate Your Findings
To ensure the validity and reliability of your analysis, seek feedback from colleagues, peers, or other researchers. Consider using member checking, a process where you share your interpretations with the original participants to confirm that your understanding aligns with their intended meaning. Member checking is crucial in validating thematic analysis findings as it ensures that the participants' perspectives are accurately represented.
This step can help you refine your analysis and strengthen the credibility of your findings.
Cherry-Picking Data: Avoid selecting only the data that supports your preconceived notions or research questions. Be open to all perspectives and interpretations.
Data Bias: Data bias can significantly impact thematic analysis by skewing the results and leading to inaccurate conclusions. It is crucial to recognize and mitigate data bias to ensure a comprehensive and balanced analysis.
Oversimplifying Complex Themes: Don’t reduce complex themes to simple labels. Capture the nuances and subtleties of the data.
Ignoring Negative Cases: Don’t overlook data that contradicts your emerging themes or research questions. Negative cases can provide valuable insights and challenge your assumptions.
Don't Just Analyze Data, Understand It with Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is a versatile and powerful tool for uncovering meaningful insights from qualitative data analysis. By systematically identifying and interpreting patterns and themes, researchers and businesses can gain a deeper understanding of complex phenomena, make informed decisions, and drive positive change. Understanding coded data insights is crucial in thematic analysis as it helps in identifying significant patterns and trends within the coded data, leading to more accurate and actionable conclusions. Thematic analysis is a method used to identify, analyze, and report patterns (themes) within qualitative data analysis.
Whether you’re conducting academic research, market analysis, exploring social issues, or seeking to improve customer experiences, thematic analysis can provide the insights you need to succeed. By following the tips and best practices outlined in this guide and leveraging the power of AI-powered tools like Thematic, you can unlock the full potential of your qualitative data and achieve your research or business goals.
Ready to dive into thematic analysis and uncover the hidden meaning in your data? Try Thematic today and experience the power of AI-driven insights.
Stay up to date with the latest
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.